Understanding the type of dual battery isolator can provide several benefits, especially if you have a dual battery system in your vehicle or another application where it’s used.
Dual battery isolators are devices that allow you to manage and isolate two separate battery systems, typically one for starting the engine (the primary or cranking battery) and another for auxiliary power (the secondary or deep-cycle battery).
Here are the three main types of battery isolators commonly used:
Diode Battery Isolators:
- Pros: Diode battery isolators are relatively simple and affordable. They use diodes to create separate electrical paths for each battery, allowing current flow in one direction only. They are suitable for low to moderate power applications.
- Cons: Diode battery isolators introduce a voltage drop across the diodes, which can reduce the charging voltage reaching the batteries. This can result in slower charging times and slightly lower voltage available to the connected devices.
Solenoid Battery Isolators
- Pros: Solenoid battery isolators, also known as relay isolators, use electromechanical relays or solenoids to control the charging and isolation of batteries. 12v Battery isolator relay offer minimal voltage drop, providing efficient charging to the batteries. They are typically more robust and can handle higher power applications.
- Cons: Solenoid battery isolators require power from the vehicle’s electrical system to activate the relays, which can create a small continuous power draw. If the vehicle’s main battery is drained or disconnected, it may prevent the relay battery isolator from functioning correctly.

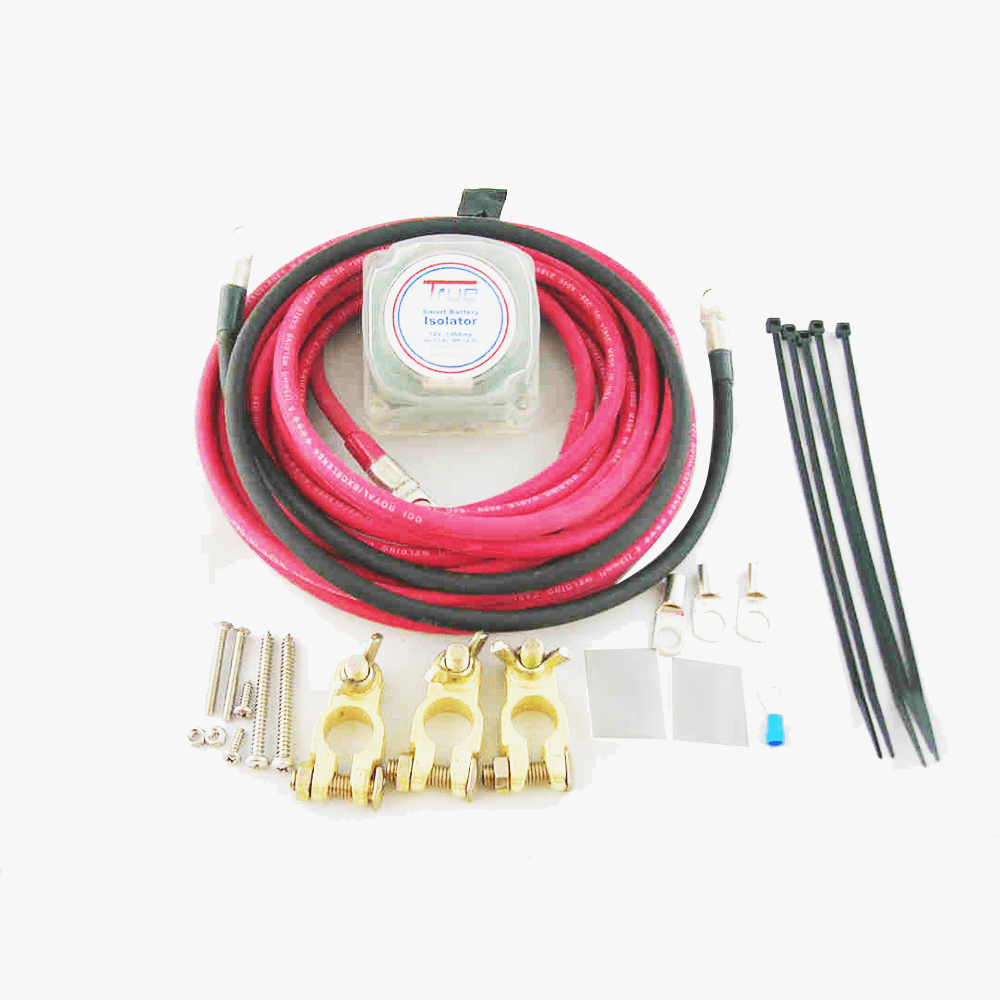
Voltage Sensitive Relay for Battery Isolator by TrueAm
Solid-State Battery Isolators:
- Pros: Solid-state battery isolators use electronic components, such as MOSFETs or FETs, to control the charging and isolation process. They offer efficient power transfer, minimal voltage drop, and faster switching compared to diode-based or solenoid-based isolators. They are suitable for a wide range of power applications and are more compact in size.
- Cons: Solid-state isolators are typically more expensive than diode-based or solenoid-based isolators. Some solid-state isolators may require additional wiring or control modules for proper operation. This could be complicated that only expert electrician can understand.
When choosing a battery isolator, consider the following factors:
- Power Requirements: Determine the power needs of your system to ensure the battery isolator can handle the required current.
- Voltage Drop: Consider the impact of voltage drop on your specific application and choose an isolator that minimizes this effect. TrueAm® dual battery isolator is known for NO voltage drop unit.
- Reliability and Durability: Assess the durability and longevity of the isolator, especially if you plan to use it in demanding environments. TrueAm® dual battery isolators are maintenance free technology. The casing design is guaranteed to be anti-vibration while the cables are ensured to be water-resistant.
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for compatibility with your specific vehicle and electrical system. Contact TrueAm® expert for battery isolator compatibility with your vehicle.
It’s important to select a battery isolator that suits your specific needs and consult the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation and usage.
(Visited 826 times, 1 visits today)